![]()

On October 4, 1958 the Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite into space called Sputnik 1. It was the size of a basketball and weighted only 183 pounds. Sputnik 1 orbited the Earth for 90 minutes and was the start of the International Space Race.
The Space Act of 1958 created the National Aeronautics Space Administration, more commonly known as NASA, on October 31, 1958. The Space Act states that NASA was established to provide for research into problems of flight within and outside the Earth's atmosphere and for other purposes. It was mainly created for reasons of national security because the Soviet Union already had a satellite and we didn't.

National Aeronautics and Space Administration logo
The United States quickly started working on our own satellite. Then, on January 31, 1958, we launched Explorer 1. It's job was to document the existence of radiation zones around the Earth. Not too much later, we launched Echo 1 on August 12, 1960. Based on Echo 1 successes, Echo 2 was launched January 25, 1964. Communications was the most successful enterprise in space.

Freedom 7 Mission Patch
Our first major undertaking was announced October 7, 1958 called Project Mercury. Project Mercury's goals were to orbit a manned spacecraft around Earth, study man's ability to work in space, and to recover both man and spacecraft safely. On May 5, 1961, Alan B. Shepard was the first man to be in space. Mercury had a total of six flights between 1961 and 1963.
The Outer Space Treaty was passed by Congress in 1967. It was the "treaty on principles governing the activities of states in the exploration and use of outer space including the moon and other celestial bodies." This treaty was the beginning of the Apollo program.
The goals of the Apollo program were to establish the technology to meet other national interest in space, to achieve preeminence in space flight for the United States, to carry out a program of scientific exploration of the moon, and to develop man's ability to work in lunar environments.

Apollo missions patch
The first Apollo flight was originally called AS-204, but after a fire in the command module during a routine launch test January 27, 1967, it was renamed Apollo 1. The fire killed three astronauts: Edward H. White, Virgil Grissom, and Robert B. Chaffee. Despite this, Apollo 7 was the first Apollo flight to fly on October 11, 1967.
Apollo 11 finally put man on the moon. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin Jr. were the first men to walk on the lunar surface. Armstrong said, "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind," as he walked on the Sea of Tranquility, which was their landing site.

Neil Armstrong walking on moon
Apollo 13 is now known as the successful failure. When the three astronauts onboard were over 320,000 kilometers from Earth NASA heard, "Ok, Houston, we've had a problem here," come over the radio. An oxygen tank blew up and severely damaged the service module and left the command module without power or air. The three astronauts on board had to move into another part of the spacecraft that was only designed for two men. Despite all the difficulties they orbited the moon and landed safely back on Earth. This proved that NASA's equipment worked very well when things went wrong.
When onboard Apollo 15, Alfred Worden performed the first space walk outside of the Earth's orbit. Apollo 17, launched on December 7, 1972, carried the last man to the moon...so far. All together there were three missions that orbited the moon (including Apollo 13), six missions that landed on the moon, and twelve astronauts to walk on the moon. The Apollo program cost about $24.4 billion.
Skylab was the first American space station. It was launched into orbit May 14, 1973. Skylab was designed for long duration missions, and it proved humans could live and work in space. It also expanded knowledge of solar astronomy. Skylab's work volume was 12,700 feet, and its overall length was 117 feet. It was manned 171 days by three astronauts.
The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project or ASTP, began in 1975. It was the first test flights that were operated by two nations, the United States and Soviet Union. It was designed to test the compatibility of rendezvous and docking systems for the United States and Soviet Union spacecraft.

Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission patch
The Mariner space probe missions were sent to Mars, Venus, and Mercury. Mariner 1 was failure but Mariner 2 was the first space probe to fly by a planet when it passed Venus on December 14, 1962.
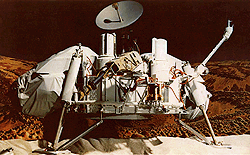
Viking 1 Lander
On August 20, 1975, NASA launched Viking 1 to go to Mars. It was designed to send back high resolution images of Mars surface, characterize the structure and makeup of Mar's atmosphere and surface, and look for any form of life. Viking 1 landed on Mars' Chryse Planitia on June 19, 1976. The Viking missions provided the most complete view of Mars. Next NASA launched Viking 2 on September 9, 1975. It landed on Mars' Utopia Planitia on August 7, 1976.
The Voyager missions are the only spacecraft to visit Uranus and Neptune. They've also been to Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 1 and 2 were launched in the summer of 1977. They are the farthest man-made objects away from Earth. They are on their 25th year of being in space and now they are continuing outside the Solar System.
The Pioneer missions also visited the outer planets. Pioneer 10 and 11 flew by Jupiter and Saturn between 1972 and 1979. Now they are continuing outside the Solar System.

Artist concept of Saturn
(artist unknown)
The main objective of all the planetary probes were to photograph the planets, get information about the atmospheres, temperatures, composition of many objects, and simply explore.
Today NASA is still very successful and powerful. They still use the same models of equipment that they used years ago such as the Saturn V rockets that launched the very first missions. This proves how successful NASA has been and hopefully will be in the future.
Krystle Thompson
8th American History
Rossville Jr. High
Post-World War 2 America Project
May 2002