Dachau
March 20, 1933 Heinrish Himmler, SS leader and chief of the Munich Police,
announces the opening of the Dachau Concentration camp. The camp was formed
by members of the SA and SS. The camp is located 10 miles northwest of
Munich in southern Germany. Dachau is one of the first camps the Nazis ever
made. The first prisoners arrived two days later. They are mainly communists
and Socialists and other political opponent of the Nazi party. The SS men
wake up the prisoners in the middle of the night. The words of the Commander
were “they are not people, they are only second class.” First there was only
60 SS men, then it grew to 238 by April 30th. The first murders were
committed the very next day after the SS took over by the SS. During the
following months of the year 1,933 other prisoners of Dachau are murdered.
“Shot on the run” or “suicide” is the process of the SS about their death.
Dachau is the only camp to remain in operation from 1933 until 1945.
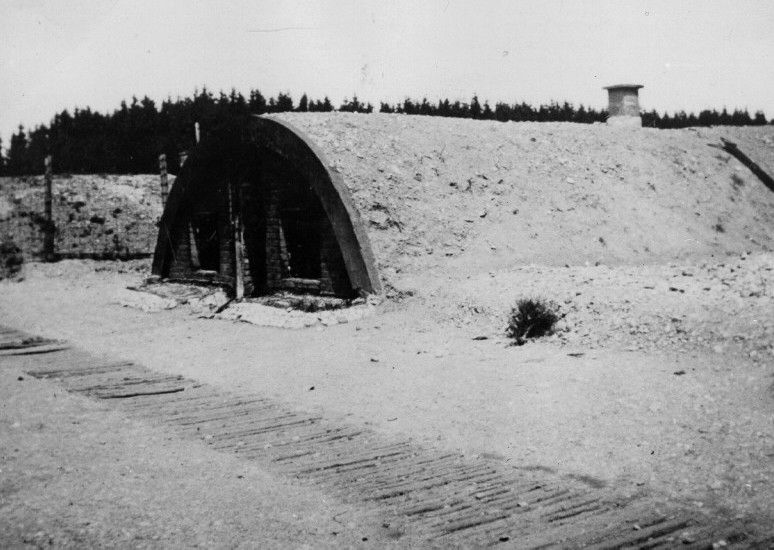
Gas Chamers were built and exist to this date. Most visitors to the Dachau
camp, by the horror to the main entrance of the large room designed as a
disguised gas chamber, rarely wonder beyond these areas. The chamber is
located next top the funeral room, which in turn connects to the large area
housing the four huge furnaces. The gas chambers are small, narrow, with low
ceilings. Once it was completed operators would simply open the outer doors
and let out the remaining gas and let it spread without risk into the
atmosphere were used for this.
| May 25, Late in the night the SS kills a Dachau camp prisoner Sebastian Nefzger, a schoolmaster from Munich. The SS report that his death was from suicide. However inspection reveals that suffocation or strangulation was the likely cause of death. Most of all it’s Hartinger who makes life difficult to the SS. On June 1, he files a suit against the camp[ commander Hilmar Wackerle “because of the crime of physical injury resulting in death.” The debate will force Himmler to remove Waeckerle from his post. Adolf Himmler will order an end to all legal happenings in Dachau. All concentration camps will be formally removed from judicial oversight and the SS will have unlimited authority over camp prisoners. In the meantime the inmates grow worse dramatically. |
|
|
dachau gas chamber |
On October 1, Theodor Eicke, the new commandor of Dachau, issues camp
regulation for prisoners and guards under his command. The orders to lay
down severe punishments, including having beatings and execution for a
violation of camp rules. Eicke establishes the death penalty on prisoners
for acts of sabotage, attemted escape, and political urging in the camp.
Eicke’s system of punishments an organization will become the model or all
concentration camps under the organization of the SS.
|
On August 15, 1938, another dramatic change takes place; the old concentration camp, which still had consisted of the buildings from the material factory, is torn down for the building of a SS military training base and the spreading of the Dachau concentration camp. It no longer meets the safety and requirements of the SS. The SS requires prisoners to work at double speed seven day a week to complete the building of the training base.
September 27, 1939,
the SS completes the transfer of all prisoners in Dachau to the Buchenwald,
Mauthausen, and Flossenburg camps. The faculties at Dachau are temporarily
converted for use by the Waffen-SS, which sets up and begins training the
Deaths Head Division which is a type fight unit pertaining to made up of
engages from concentration camp guards. The Dachau concentration camp will
resume operations in February 1940. September 3, 1941, SS doctors arrive at
Dachau to begin the regular selection of prisoners they judge to be ill or
weak to work. These prisoners will be transferred to Hartheim and killed
there. Hartheim in Austria, is a killing site, where medical staff gas
concentration camp prisoners as part of an operation code-named “Special
Treatment 14f13.” From January 1942 until November 1944, SS doctors will
select more than 3,000 Dachau prisoners to be killed at Hartheim. November
15, 1941, the SS Inspection of concentration camp justifies the defer of the
execution of Soviet prisoners of War (POWs) in Dachau and other
concentration camps if SS doctors certify to their fitting for work. In
light of the severe labor shortages in Germany the SS decides to alter the
Commissar Order, which required the Soviet political commissars and other
officials. The German Army turned tens of thousands of Soviet prisoners for
forced labor, it continues executing Soviet POWs will be transferred to
Dachau between Fall of camp. June 3, 1942, almost 60 Polish priests and
monks arrive at Dachau from the Auschwitz camp in occupied Poland, are
imprisoned in Dachau during the camps existence. The Germans attempt to
undermine the leadership of the catholic church in Poland as part of their
plan to Germanize occupied Poland. The SS holds Catholic clergy together in
Barrack 26, the so-called “Priest Barracks” in Dachau.
|
|
|
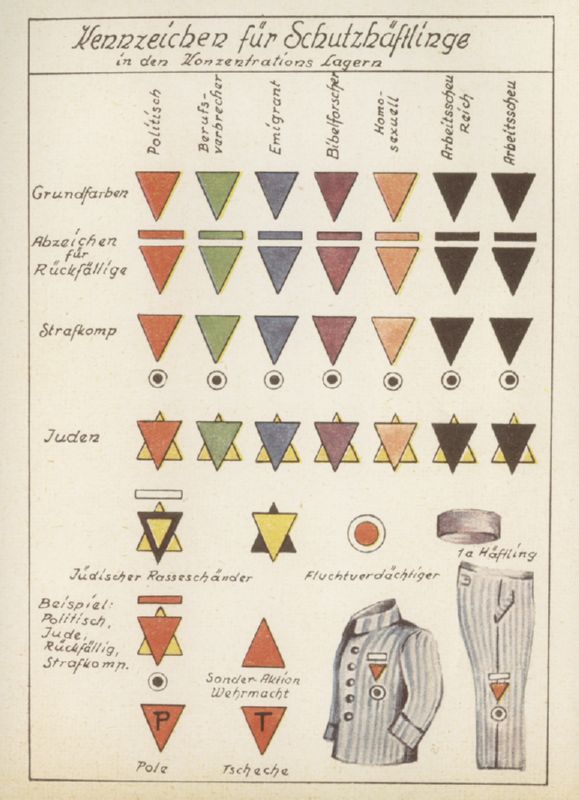
chart of prisoner markings |
April 26, 1945, just three days before the liberation of the Dachau camp,
the SS forces about 7,000 prisoners on a death march from south of Dachau to
Tegernsee. During the six day death march the SS shoots anyone who cannot
keep up or continue. Many others die of exposure, hunger, and exhaustion.
The surviving prisoners will arrive in Teensier on May 02, where American
forces free them.
| April 29, American forces cleared the camp of Dachau where they found more than 30 coal cars filled with rotting bodies. American soldiers find more than 30,000 prisoners in the camp. There were more than 200,000 registered prisoners during the history of the camp. Of these more than 30,000 died. Because thousands more prisoners arrived and died in the camp without being registered, the total number of victims remain unknown. |
American soldiers discover dead bodies in a coal car
|
Macy Gillum
7th Social Studies
Rossville Jr. high
Holocaust project
Spring 2009